Risk is an integral part of business. Without risk there is no oppurtunity for rewards or returns. Act of doing Business is in itself retaining 'good' risk & getting rewarded (ROI) for the same. Enterprise of all types and sizes face internal and external factors and influences that make it uncertain whether and when they will achieve their objectives. The effect this uncertainity has on an enterprise's objective is "Risk".
Enterprise Risk Management is a structured approached of Identifying and Evaluating risks which affect the objectives of the enterprise, then decide on whether to terminate, tolerate, treat or transfer the risk.
Risk Managers from BimaGenieTM would develop and implement Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Program as per the principles and guidelines of ISO 31000:2009, which would not only make the operating personnel aware of the objectives of the management and potential risks which can affect the objectives at various degrees, but also the strategies to be adopted. This will provide comfort to all stakeholders that exposures are being managed well and risk impacts are kept at tolerable level.
Each specific sector or application of risk management bring with it individual needs, audiences, perceptions and criteria. Therefore, a key feature of ISO 31000:2009 is the inclusion of "establishing the context" as an activity at the start of this generic risk management process. Establishing the context will capture the objectives of the organization, the environment in which it pursues those objectives, its stakeholders and the diversity of the risk criteria - all of which help reveal and assess the nature and complexity of its risks.
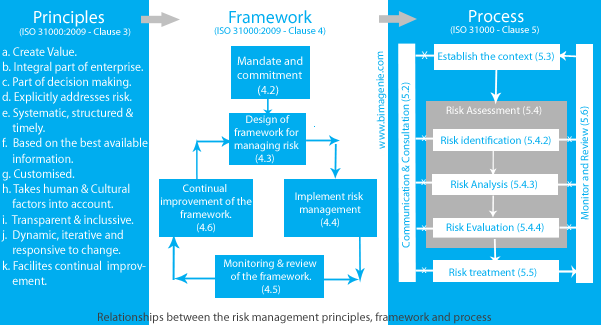
The relationship between the principles for managing risk, the framework in which it occurs and the risk management process is shown below.
When Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Program is implemented and maintained in accordance with ISO Standard, the management of risk enables an organization to, for example:
a. increase the likelihood of achieving objectives;
b. encourage proactive management;
c. be aware of the need to identify and treat risk throughout the organization;
d. improve the identification of opportunities and threats;
e. comply with relevant legal and regulatory requirements;
f. improve mandatory and voluntary reporting;
g. improve governance;
h. improve stakeholder confidence and trust;
i. establish a reliable basis for decision making and planning;
j. improve controls;
k. effectively allocate and use resources for risk treatment;
l. improve operational effectiveness and efficiency;
m. enhance health and safety performance, as well as environmental protection;
n. improve loss prevention and incident management;
o. minimize losses;
p. improve organizational learning; and
q. improve organizational resilience.